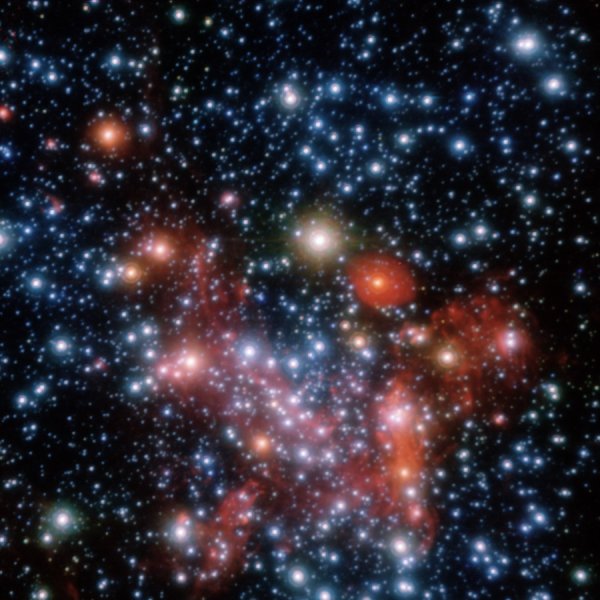
At the center of our Galaxy lies an extremely dense concentration of massive stars near the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A*. These stars – giant and short-lived – have a decisive influence on their surroundings and on how the black hole accumulates mass. New work, in which experts from ASU played an important role — the lead author is Dr. Alex C. Gormaz-Matamala from the Stellar Department — presents the latest models of the evolution of these massive stars based on modernized mass loss prescriptions. It appears that the models commonly used to date may have significantly overestimated mass loss in the early stages of stellar evolution. The work thus offers an updated view on the interpretation of observed star populations in the center of our Galaxy.
Continue reading: ASU website (in Czech)
Image description: Image of a core star cluster taken by the NACO instrument on the Very Large Telescope in Chile (ESO). In addition to bright hot stars, dust and gas structures are also visible, complementing the complex environment at the center of our Galaxy. © ESO
More informations
- Popular article: Na čem pracujeme: Jak změna modelů hvězdných větrů přepisuje příběh hvězd u Sagittarius A* (M. Švanda, ASU, in Czech)
- Scientific paper: A. C. Gormaz-Matamala a kol., Revisiting the Evolutionary Status of Massive Stars at the central parsec of the Milky Way, Astronomy & Astrophysics in press, preprint arXiv:2512.07432
- Contact: Dr. Alex C. Gormaz-Matamala, alex.gormaz@asu.cas.cz